Understanding Metformin
- Jason Cafer MD

- Jun 21, 2025
- 4 min read
Updated: Jun 21, 2025
Metformin is a safe and widely recommended add-on for managing weight gain and metabolic issues caused by psychotropic medications. Its mechanism is surprisingly intriguing—and even bears a biochemical resemblance to cyanide.
This content is from the forthcoming book: Cafer's Psychopharmacology 2nd Edition Series: Prescribing Lithium

Pronunciation: met-FOR-min (GLOO-ko-fahj)
Mnemonic phrase: “Met formin’ Glucose fudge”
Classification: Biguanide anti-hyperglycemic
FDA Approved for: Diabetes mellitus, type 2
Available strengths:
❖ ER: 500 & 750 mg
❖ IR: 500, 850, &1000 mg
Metformin song (10 versions): YouTube Music
Used Off-Label for:
❖ Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
❖ Antipsychotic-induced weight gain
❖ Weight loss
❖ Prevention of type 2 diabetes (prediabetes)
❖ Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
❖ Gestational diabetes
❖ Type 1 diabetes (to ↓ insulin requirements)
❖ Longevity (investigational)
Metformin Basics
❖ First-line type 2 diabetes medication
❖ Low risk of hypoglycemia, even in non-diabetics
❖ Plasma half-life: ~ 5 hours
❖ Elimination half-life (from tissues): ~20 hours
Weight Management
❖ First-line for antipsychotic-induced weight gain
➤ may mitigate prolactin elevation
❖ Metformin found slightly more effective than topiramate (Maayan et al, 2010)
❖ GLP-1 agonists are the most effective
Longevity
❖ In animal models
➤ slows biologic aging process
➤ decreases incidence of cancer
❖ Appears to prevent cognitive decline with aging (Ng et al, 2014)
❖ Targeting Aging with Metformin (TAME) controlled trial is in progress
➤ longevity benefit in humans unproven
Side Effects
❖ Diarrhea – 50% IR, 10% ER formulation
❖ Nausea – 25%
❖ Flatulence – 10%
❖ Vitamin B12 (cobalamin) deficiency – 3–30%
❖ May blunt muscle growth in response to strength training
➤ metformin’s activation of AMPK antagonizes mTOR signaling, which is essential for muscle protein synthesis and hypertrophy
BLACK BOX WARNING: Lactic Acidosis
❖ Potentially fatal
➤ FDA has relaxed the warning for patients with stable renal function
❖ ~33% risk with large overdose
❖ Extremely rare in healthy individuals
➤ near-zero risk with eGFR > 30 mL/min (Lipska et al, 2011)
❖ Heavy alcohol consumption increases the risk of lactic acidosis
⭐ Avoid in patients with serious medical illness

Principal Mechanism – Sequence of Events
❖ Metformin inhibits mitochondrial Complex I → slows the electron transport chain → decreases ATP production → cell senses energy depletion → activates AMPK (AMP-activated protein kinase) = master regulator of cellular energy → shifts metabolism toward energy conservation:
➤ ↓ glucose production by the liver
➤ ↑ insulin sensitivity of body tissues
➤ ↓ fat accumulation
➤ ↑ mitochondrial biogenesis
❖ Metformin creates mild energy stress inside cells (especially liver, gut) → reprograms the body’s metabolism to:
➤ use energy more wisely
❖ Example of hormesis
➤ low doses of a stressor stimulate beneficial adaptive responses, while higher doses are harmful
Mechanistically-Related Drugs
❖ Berberine (nutritional supplement) has the same basic mechanism: mild inhibition of mitochondrial Complex I → AMPK activation
❖ Cyanide (poison) completely inhibits mitochondrial Complex IV → cellular hypoxia → severe lactic acidosis → multi-organ failure and death

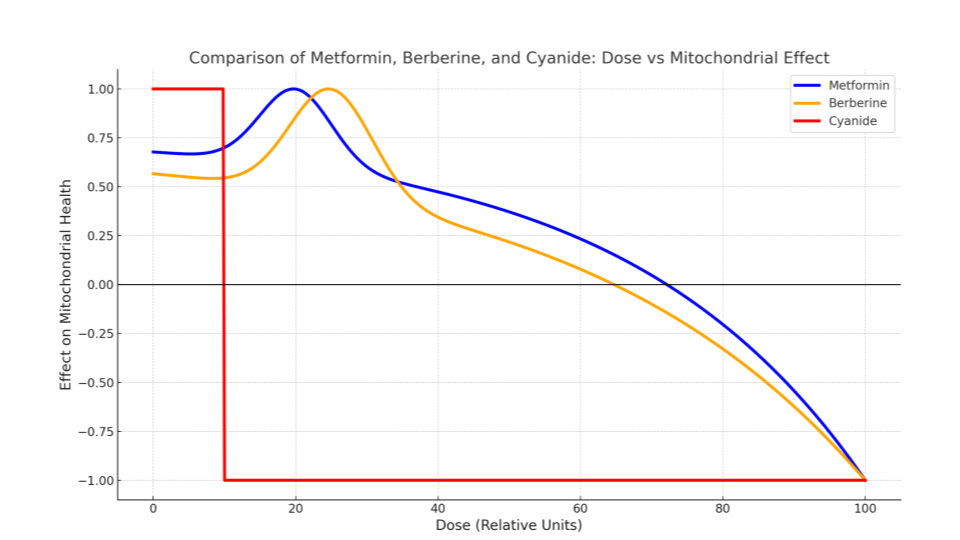
Additional Mechanisms
❖ Reduces intestinal glucose absorption
➤ modulation of gut microbiota
➤ enhanced GLP-1 secretion
Overdose
❖ Mitochondrial Complex I inhibition → energy crisis (low ATP) → lactic acidosis (~33%)
❖ Hypoglycemia in ~10% of cases
❖ Survival is common with aggressive support (IV fluids, hemodialysis)
Potential Benefits as Lithium Adjunct
❖ Weight management
➤ while lithium is less likely to cause weight gain than most alternatives (valproate, quetiapine), weight gain is a commonly cited reason for lithium discontinuation
❖ Reversal of insulin resistance
➤ brain insulin resistance may contribute to bipolar mood destabilization (TRIO-BD study)
❖ Protection against lithium-induced vasopressin resistance (animal models)
✅Monitoring
❖ Baseline: eGFR, LFTs, B12, HbA1c, weight
❖ Routine: eGFR (annual, q3–6m if <60), B12 (q2–3y), HbA1c (q3–6m if diabetic)
❖ Situational: lactate if acidosis suspected, electrolytes if severe illness
❖ Acidosis on metabolic panel is evidenced by low bicarbonate (listed as CO₂)
❖ Signs of acidosis are nonspecific with subtle onset, including malaise, myalgias, abdominal pain, respiratory distress, or somnolence
❖ Signs of B12 deficiency
➤ macrocytic anemia, neuropathy, glossitis
❖ Hemoglobin A1c
➤ normal 4.0–5.6%
◇ average glucose of 100 → A1c 5.1%
➤ prediabetes 5.7–6.4%
➤ diabetes ≥ 6.5%
◇ average glucose of 200 → A1c 8.6%
◇ average glucose of 300 → A1c 12.1%
Dosing
🟥 Not recommended if eGFR < 45 mL/min
🟥 Supplement Vit B12 (500–1000 mcg) and calcium (1200–1500 mg) if B12 low or borderline
▶️ For type 2 diabetes (FDA dosing) – IR
➤ Start 850 mg QD or 500 mg BID with meals
➤ Increase by 500 mg/day q week or 850 mg/day q 2 wk as tolerated
➤ Target of 850–1000 mg BID
➤ Max of 2550 mg/day (3 x 850 mg)
🔴 Change to ER form if diarrhea or GI distress
▶️ For type 2 diabetes (FDA dosing) – ER
➤ Start 500 mg ER or 750 ER q PM
➤ Increase by 500 mg/day q week as tolerated
➤ Target of 1000–2000 mg ER q PM
➤ Max of 2000 mg ER / day
➤ May add 500 mg IR if inadequate
▶️ For weight management (off label)
➤ Same as DM2 dosing
▶️ For longevity (investigational)
➤ The TAME longevity study is using 1500 mg of metformin ER
➤ Some taking metformin for longevity skip it on weight training days because it may blunt muscle growth
🟥 Hold treatment for surgery
🟥 Hold if restricting food/fluid
🟥 Hold for iodinated contrast study, restart after 48 hr if stable renal function
🟥 Discontinue metformin if eGFR falls below 30
Dynamic Interactions
❖ Risk of lactic acidosis, which is increased by carbonic anhydrase inhibitors (CAIs) such as dichlorphenamide > acetazolamide > methazolamide > topiramate > zonisamide
➤ risk remains theoretical and not consistently observed in clinical practice
Kinetic interactions
❖ Excreted unmetabolized in urine via active tubular secretion, primarily by OCT2 and MATE-1 transporters
➤ Dual OCT2/MATE-1 inhibitors increase metformin serum levels ~35–50%
◇ cimetidine (Tagamet)
◇ pyrimethamine (Daraprim)
◇ trimethoprim (in Bactrim with SMX)
◇ vandetanib (Caprelsa) > crizotinib (Xalkori)
◇ dolutegravir (in HIV combos)


Copyright 2025 CaferMed Publishing



i really enjoyed this simplified format of drug info. thanks.